Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the seventh element in the periodic table and is classified as a nonmetal. It is a diatomic gas (N2) at room temperature and makes up about 78% of the Earth's atmosphere by volume.
Atomic Structure
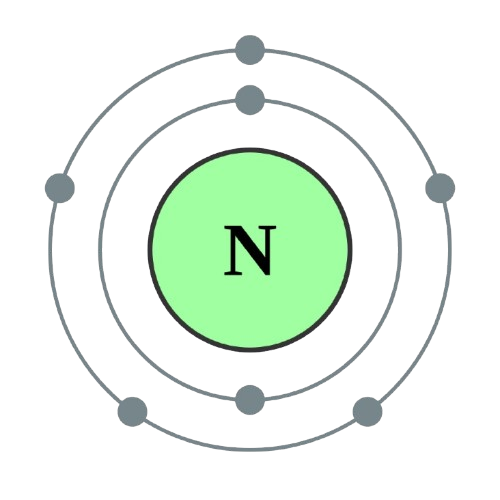
Atomic Information
| Property |
Value |
| Atomic Number |
7 |
| Symbol |
N |
| Atomic Mass |
14.007 u |
| Electron Configuration |
1s2 2s2 2p3 |
| State at Room Temperature |
Gas |
Interesting Facts About Nitrogen
- Nitrogen gas is colorless, odorless, and tasteless.
- It is essential for all living organisms as it is a key component of amino acids and nucleic acids.
- Nitrogen gas is relatively inert and does not easily react with other substances under normal conditions.
- Compounds like ammonia (NH3) and nitrates are vital for agriculture and industry.
- Nitrogen is used in cryogenics due to its low boiling point (-196°C).
History of Nitrogen
Nitrogen was discovered in 1772 by Scottish chemist Daniel Rutherford. He demonstrated that a portion of air does not support combustion or life, which he called "noxious air." Later, it was named "nitrogen" from the Greek words "nitron" and "genes," meaning "saltpeter-forming."
Uses of Nitrogen
Nitrogen has various industrial, scientific, and agricultural applications:
- Fertilizers: Nitrogen compounds like ammonia and urea are critical for agricultural fertilizers.
- Preservation: Nitrogen gas is used to create an inert atmosphere for preserving food and sensitive materials.
- Cryogenics: Liquid nitrogen is used for freezing biological specimens and in medical procedures.
- Explosives: Nitrogen is a key component in explosives like TNT and nitroglycerin.
- Manufacturing: Nitrogen gas is used in metalworking and electronics manufacturing to prevent oxidation.

