Carbon
Carbon is the sixth element in the periodic table and is classified as a nonmetal. It is one of the most versatile elements, forming the basis of all known life. Carbon is capable of forming a vast number of compounds due to its ability to form four bonds.
Atomic Structure
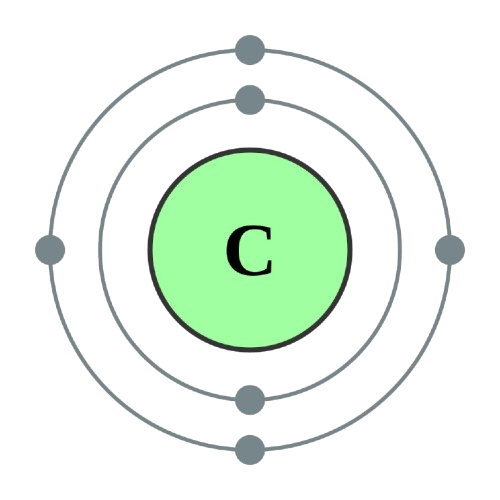
Atomic Information
| Property |
Value |
| Atomic Number |
6 |
| Symbol |
C |
| Atomic Mass |
12.011 u |
| Electron Configuration |
1s2 2s2 2p2 |
| State at Room Temperature |
Solid |
Interesting Facts About Carbon
- Carbon exists in various allotropes, including diamond, graphite, and amorphous carbon.
- Diamond is one of the hardest known materials, while graphite is soft and a good conductor of electricity.
- Carbon forms the backbone of organic chemistry and is present in all living organisms.
- Carbon can form long chains and rings, enabling the creation of millions of organic compounds.
- Carbon dating, based on the isotope Carbon-14, is used to determine the age of ancient artifacts and fossils.
History of Carbon
Carbon has been known since ancient times. Its name comes from the Latin word "carbo," meaning coal. The study of its compounds gave rise to the field of organic chemistry, as carbon is the key element in all organic matter.
Uses of Carbon
Carbon has numerous applications across various industries:
- Fuel: Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are composed primarily of carbon.
- Materials: Carbon fibers are used in lightweight, high-strength materials for aerospace and sports equipment.
- Lubricants: Graphite is used as a lubricant and in pencils.
- Steelmaking: Carbon is a key component in the production of steel.
- Biotechnology: Carbon nanostructures, like nanotubes and graphene, have cutting-edge applications in technology and medicine.

