Boron
Boron is the fifth element in the periodic table and is classified as a metalloid. It has properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals. Boron is essential for plant growth and has various industrial applications.
Atomic Structure
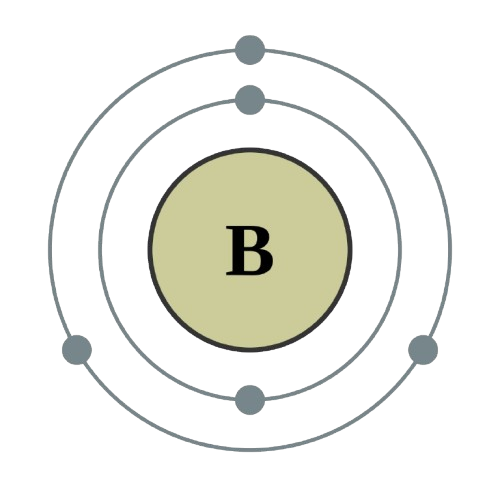
Atomic Information
| Property |
Value |
| Atomic Number |
5 |
| Symbol |
B |
| Atomic Mass |
10.81 u |
| Electron Configuration |
1s2 2s2 2p1 |
| State at Room Temperature |
Solid |
Interesting Facts About Boron
- Boron is found in the Earth's crust mainly in the form of borates, such as borax and kernite.
- It is a poor conductor of electricity at room temperature but becomes a good conductor at higher temperatures.
- Boron compounds, like boric acid, are used as mild antiseptics and in glassmaking.
- Amorphous boron is a brown powder, while crystalline boron is extremely hard and black.
- Boron is essential for plants but toxic in high quantities.
History of Boron
Boron was first isolated in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy, Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, and Louis Jacques Thénard. Its name comes from the Arabic word "buraq" and the Persian word "burah," referring to borax, a naturally occurring mineral containing boron.
Uses of Boron
Boron has a variety of applications across different industries:
- Glass and ceramics: Boron is used to make borosilicate glass, which is heat resistant.
- Agriculture: Boron is an essential micronutrient in fertilizers for plant growth.
- Detergents: Boron compounds like borax are used as cleaning agents.
- Electronics: Boron is used in semiconductors and as a dopant in silicon manufacturing.
- Space exploration: Boron fibers are used to reinforce lightweight materials in aerospace technology.

