Beryllium
Beryllium is the fourth element in the periodic table and is classified as an alkaline earth metal. It is a hard, grayish metal that is relatively rare and highly toxic in its powdered form.
Atomic Structure
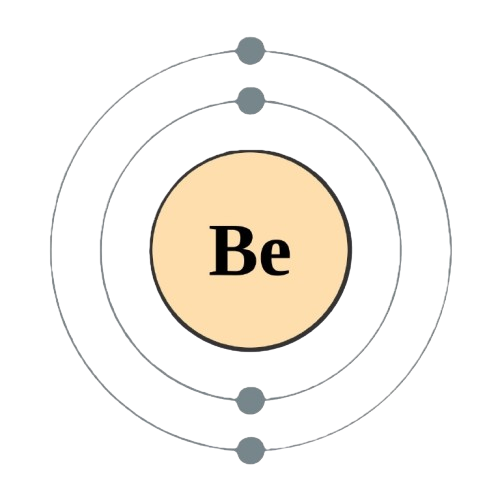
Atomic Information
| Property |
Value |
| Atomic Number |
4 |
| Symbol |
Be |
| Atomic Mass |
9.0122 u |
| Electron Configuration |
1s2 2s2 |
| State at Room Temperature |
Solid |
Interesting Facts About Beryllium
- Beryllium is lightweight but has a high melting point, making it useful in aerospace applications.
- It is nonmagnetic and has excellent thermal conductivity.
- Beryllium is transparent to X-rays and is used in the production of X-ray windows.
- It is primarily obtained from the minerals beryl and bertrandite.
- Due to its toxicity, handling beryllium requires strict safety precautions.
History of Beryllium
Beryllium was discovered in 1798 by French chemist Nicolas-Louis Vauquelin while analyzing beryl and emeralds. It was first isolated in 1828 by Friedrich Wöhler and Antoine Bussy through the reduction of beryllium chloride.
Uses of Beryllium
Beryllium is valued for its unique properties and is used in various industries:
- Aerospace: Used in lightweight structural components for aircraft, satellites, and spacecraft.
- Electronics: Beryllium alloys are used in connectors, switches, and other electrical components.
- Nuclear reactors: Serves as a neutron reflector and moderator.
- X-ray technology: Beryllium is used in X-ray windows due to its transparency to X-rays.

