Lithium
Lithium is the third element in the periodic table and is classified as an alkali metal. It is a soft, silvery-white metal that is highly reactive and the lightest solid element.
Atomic Structure
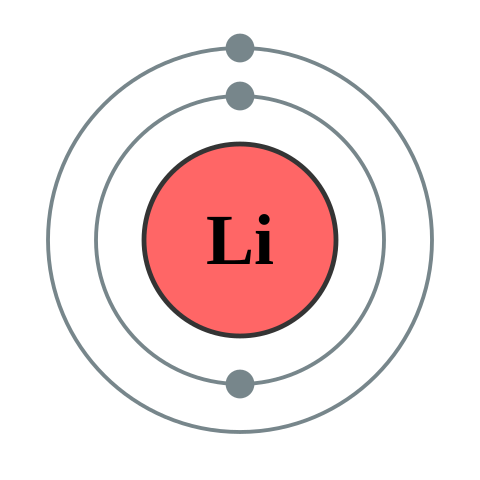
Atomic Information
| Property |
Value |
| Atomic Number |
3 |
| Symbol |
Li |
| Atomic Mass |
6.94 u |
| Electron Configuration |
1s2 2s1 |
| State at Room Temperature |
Solid |
Interesting Facts About Lithium
- Lithium is the least dense metal and can float on water.
- It reacts vigorously with water, producing hydrogen gas and lithium hydroxide.
- Lithium is used in the production of lightweight batteries, especially for portable electronics and electric vehicles.
- It is an essential component in treating certain mental health conditions, like bipolar disorder.
- Lithium does not occur freely in nature but is found in minerals such as spodumene and petalite.
History of Lithium
Lithium was discovered in 1817 by Swedish chemist Johan August Arfvedson while analyzing the mineral petalite. Its name comes from the Greek word "lithos," meaning stone, because it was first found in minerals rather than plant or animal matter.
Uses of Lithium
Lithium has numerous important applications:
- Batteries: Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
- Glass and ceramics: Lithium is used to strengthen glass and ceramics.
- Medicines: Lithium compounds are used to treat psychiatric disorders, such as bipolar disorder.
- Alloys: Lithium is used to create lightweight and strong alloys for the aerospace industry.

