Helium
Helium is the second element in the periodic table and is classified as a noble gas. It is colorless, odorless, and the second lightest element after Hydrogen. Helium is an inert gas, meaning it doesn't easily react with other elements or compounds.
Atomic Structure
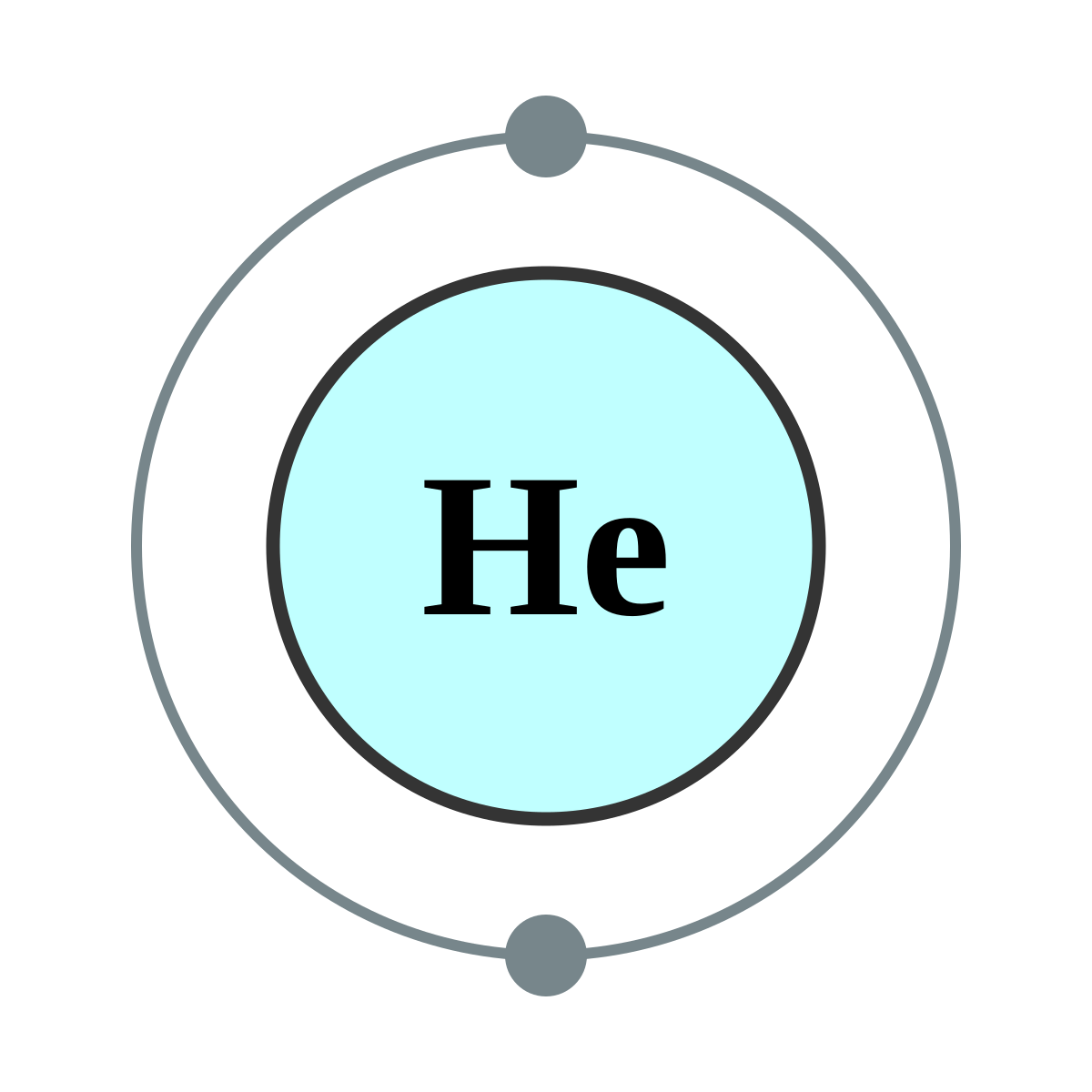
Atomic Information
| Property |
Value |
| Atomic Number |
2 |
| Symbol |
He |
| Atomic Mass |
4.0026 u |
| Electron Configuration |
1s2 |
| State at Room Temperature |
Gas |
Interesting Facts About Helium
- Helium is the second most abundant element in the universe, after Hydrogen.
- Helium is lighter than air and is commonly used to fill balloons and airships.
- It has the lowest boiling and melting points of any element.
- Helium does not solidify under standard pressure, even at absolute zero.
- The Sun produces Helium through the nuclear fusion of Hydrogen.
History of Helium
Helium was first discovered in 1868 by French astronomer Pierre Janssen and English scientist Norman Lockyer. It was identified in the Sun's spectrum during a solar eclipse before being found on Earth in 1895 by Sir William Ramsay while studying uranium minerals.
Uses of Helium
Helium has many unique and important applications:
- Cryogenics: Helium is used as a coolant for superconducting magnets in MRI scanners.
- Space exploration: Helium is used to pressurize fuel tanks and in the cooling of rocket engines.
- Breathing mixtures: Helium is combined with oxygen to create breathing gases for deep-sea diving.
- Balloon inflation: Helium is widely used to fill decorative and weather balloons.

