Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the first and simplest element in the periodic table. It is the lightest element, consisting of just one proton and one electron. Hydrogen is a non-metal and is most commonly found as a diatomic molecule, H2.
Atomic Structure
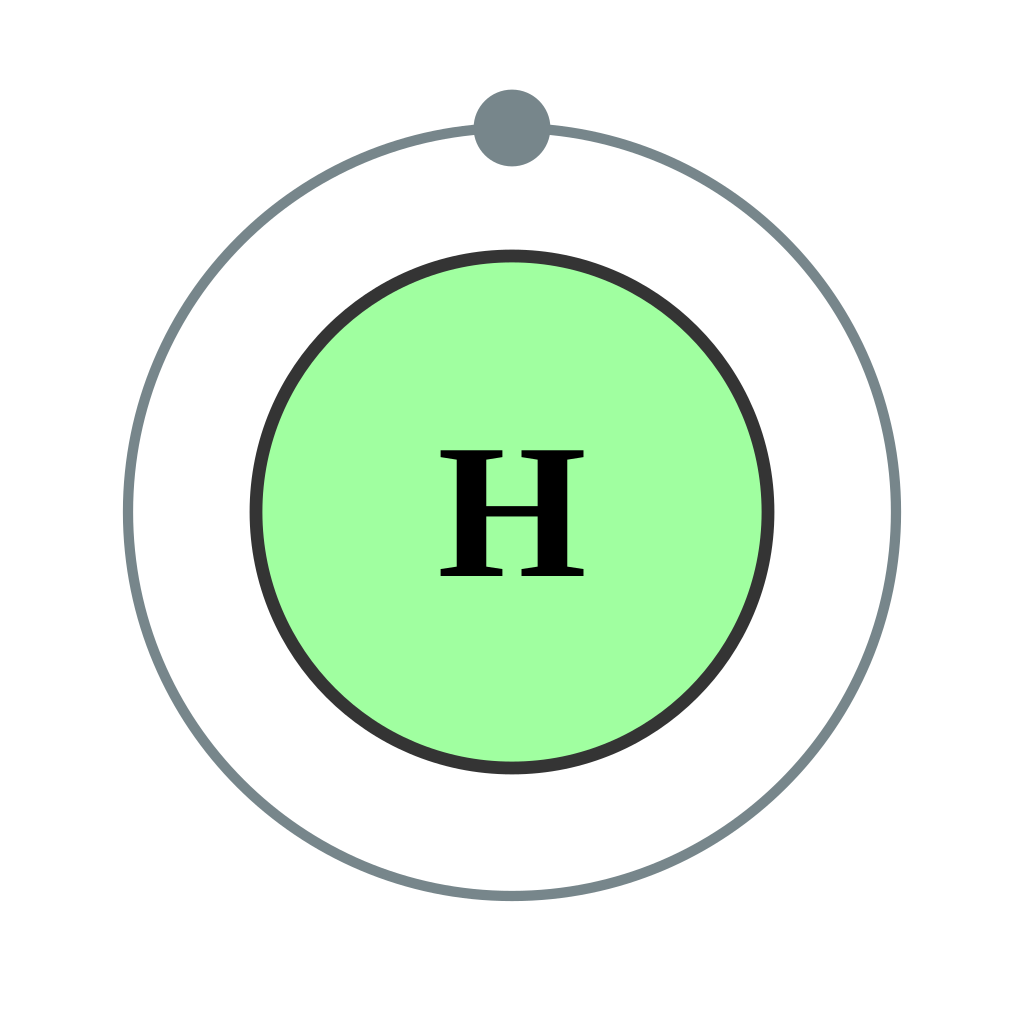
Atomic Information
| Property |
Value |
| Atomic Number |
1 |
| Symbol |
H |
| Atomic Mass |
1.008 u |
| Electron Configuration |
1s1 |
| State at Room Temperature |
Gas |
Interesting Facts About Hydrogen
- Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, making up roughly 75% of its normal matter by mass.
- Hydrogen gas (H2) is highly flammable and was used in early airships like the Hindenburg.
- In its molecular form, H2 is colorless, odorless, and tasteless.
- Hydrogen is a key component in the production of ammonia (NH3), which is vital for fertilizers.
- It plays an essential role in stars, including the Sun, where nuclear fusion occurs to form helium from hydrogen.
History of Hydrogen
Hydrogen was discovered by Henry Cavendish in 1766. He produced hydrogen by reacting metals with acids, and found that it was a unique gas that produced water when burned. Later, Antoine Lavoisier gave hydrogen its name, which comes from the Greek word "hydro" meaning water and "genes" meaning creator, because it forms water when it reacts with oxygen.
Uses of Hydrogen
Hydrogen has many applications in modern industries:
- Fuel cells: Hydrogen is used in fuel cells to generate electricity, primarily for use in vehicles and other portable devices.
- Hydrogenation: In the food industry, hydrogen is used to hydrogenate oils, turning liquid oils into solid fats, like margarine.
- Rocket fuel: Hydrogen is used as rocket fuel (liquid hydrogen) in combination with liquid oxygen for space exploration.

